Stepper motor is widely used for CNC and other automatic machinery projects. With the help of this DRV8825 stepper motor driver module, you can drive any stepper motor with just help of two pins of any microcontroller.
Today we will see in detail how this DRV8825 stepper motor driver can be interfaced with very popular Arduino board.
Features and Benefits of DRV8825 stepper motor driver
• PWM Microstepping Stepper Motor Driver
– Built-In Microstepping Indexer
– Up to 1/32 Microstepping
• Multiple Decay Modes
– Mixed Decay
– Slow Decay
– Fast Decay
• 8.2-V to 45-V Operating Supply Voltage Range
• 2.5-A Maximum Drive Current at 24 V TA = 25°C
• Simple STEP/DIR Interface
• Low Current Sleep Mode
• Built-In 3.3-V Reference Output
• Small Package and Footprint
• Protection Features pin.
– Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
– Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
– VM Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
– Fault Condition Indication Pin (nFAULT)
DRV8825 Stepper motor driver module
As this IC comes in 28 pin HTSSOP package, it is little bit difficult for hobbyist to use this IC. So this module with all necessary components and connections becomes very easy to use in our projects.
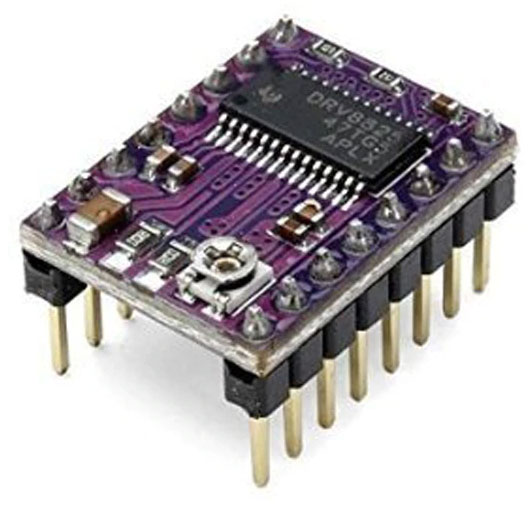


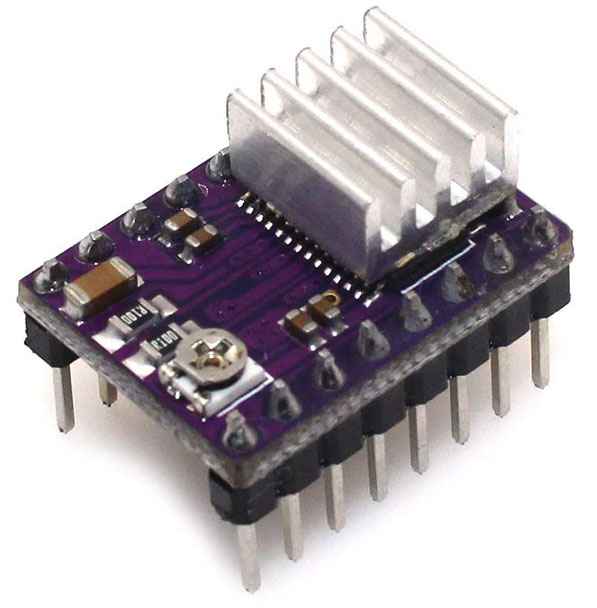
Interfacing DRV8825 stepper motor driver with microcontroller
Now, let us see how this module can be connected with any microcontroller.

Let us explore now how this module functions with its various pins.
Power connection –
The module can be powered by DC supply up to 45 V and can handle up to 2.5 Amps current at 24 V. At 45 V the current rating is up to 2.2 Amps. These pins are highlighted in following pic. Generally the voltage will be between 8 and 45 Volt DC.
It is recommended to place a bulk power supply capacitor like 100 mfd near to power supply pins to smooth out current surges during driving of a stepper motor.
Please see that your power supply is rated at least 30% more than the maximum current that can be supplied to your stepper motor. Consult the manufacturer’s datasheet for this value.

Stepper motor connection
Each bipolar stepper motor generally has 4 connection wires that connects to two internal windings of the motor. For example the following figure shows a typical NEMA 17 stepper motor.

A typical bipolar stepper motor has following specifications –

Following figure shows the connection diagram of a stepper motor and also its working principle.
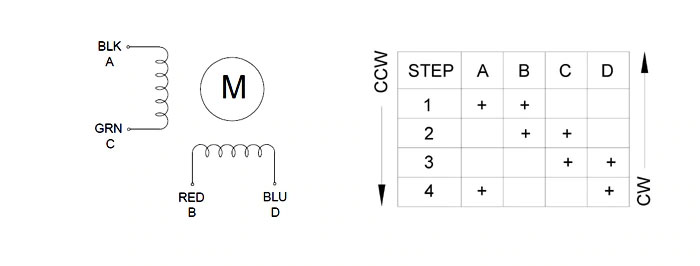
The stepper motor has to be connected to the DRV8825 Stepper motor driver module as follows.

Ok. After understanding the stepper motor connections, let us see how the power to DRV8825 stepper motor driver module is supplied.
Logic power supply
DRV8825 uses the motor power supply to power itself so unlike A4988 stepper motor IC , no other external power has to be applied. Only Gnd of the logic supply has to be provided as shown below.

After learning how the DRV8825 stepper motor driver can be connected to stepper motor, let us see how the motor can be controlled . This is done by properly handling the left hand side pins of the module.
Stepper motor control
Following pins show the most important part of the module as far as controlling the stepper motor is concerned – the Direction pin and Step pin.
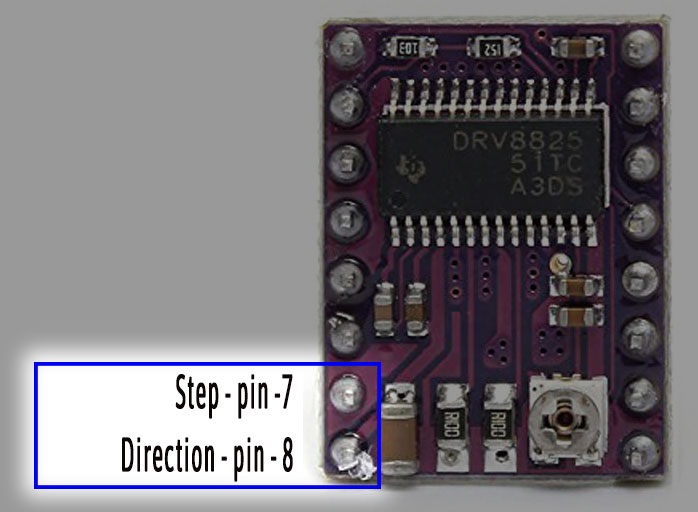
Power control
Now let us understand power controlling pins. By this pins you can control the power to the module.
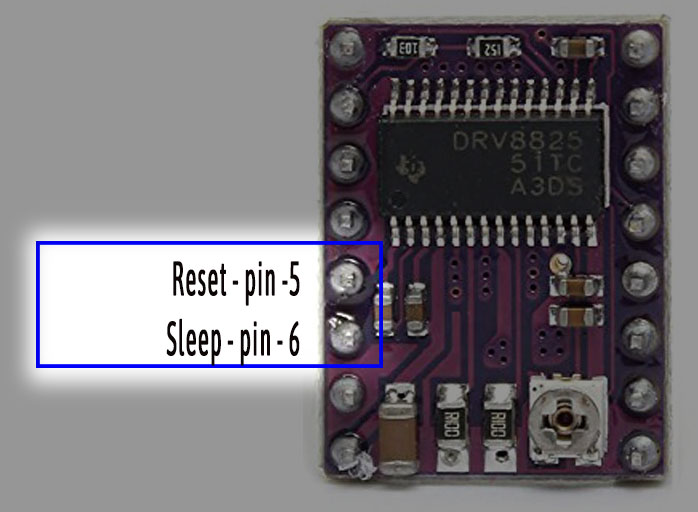
Fifth pin is Reset pin. It is also active low. By pulsing this pin low, you can place the stepper motor in Home position.
Sixth pin is Sleep pin. It is active low. By making this pin low makes this module sleep and the thus the power consumption can be reduced at lowest level.
Step selection
Most of the stepper motor has step angle of 1.8 degree. That means if you turn it for one step, the axis of the motor will turn 1.8 degree either clockwise or anticlockwise depending upon voltage level at Direction pin.
So for turning of one complete circle or one round will require such 200 steps. That means if you supply 200 pulses to the Step pin, the axis of motor will turn one full circle.
Now what if we want to turn the axis little bit finer… may be at 0.9 degree per step or may be half of that ? Fortunately , you can do it. Yes, the module can help you to have 1/2 , 1/4, 1/8 , 1/16 and 1/32 steps per one pulse input.
It is called microstepping and it is a rather complex process energizing the coils with proper current levels. But by using this module it becomes very easy to choose how much steps you want stepper motor to have one revolution.
Just choose the appropriate pins and there you have it !
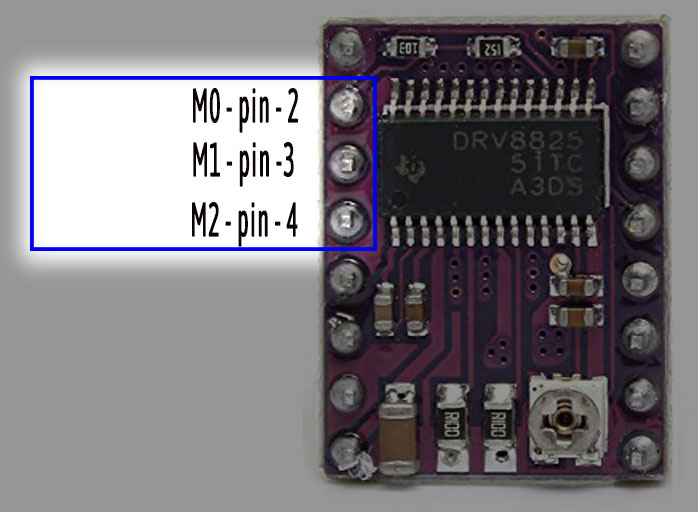
By setting appropriate logic levels, you can choose the size of one step or in other way – you can choose number of total steps for one complete revolution. It is as under –

All these three pins are pulled internally low, so if you keep these pins disconnected or floating, the step resolution will be 1 and total steps per revolution will be 200.

The final pin is Enable pin. This pin is also active low. It is internally pulled low so by default. The Enable pin is used to control the output drivers and enable/disable operation of the indexer. When Enable pin is low, the output H-bridges are enabled, and rising edges on the STEP pin are recognized. When Enable is high, the H-bridges are disabled, the outputs are in a high-impedance state, and the STEP input is ignored.
There is also a Fault output pin, which becomes low whenever the H-bridge is disabled due to over current protection or thermal shutdown. By monitoring this pin, we can have a feedback of any fault occurring during operation of stepper motor driving.

So now you know properties of each pin and how you can utilize them for controlling of any stepper motor.
Current setting
Let us take one final step to start using this DRV8825 Stepper motor driver module.
Torque capacity of each type of stepper motor is different depending upon their construction. This determines how much maximum load they can turn per revolution. Which, in turn depends on how much current can be applied to each of the coil – also called rated current of the motor.
DRV8825 stepper motor driver module has one preset provided to set this maximum current value that can be applied to connected stepper motor.

As per datasheet of DRV8825 IC –
The current through the motor windings is regulated by a fixed-frequency PWM current regulation, or current chopping. When an H-bridge is enabled, current rises through the winding at a rate dependent on the DC voltage and inductance of the winding.
Once the current hits the current chopping threshold, the bridge disables the
current until the beginning of the next PWM cycle. In stepping motors, current regulation is used to vary the current in the two windings in a semi-sinusoidal fashion to provide smooth motion.
The PWM chopping current is set by a comparator which compares the voltage across a current sense resistor connected to the xISEN pins, multiplied by a factor of 5, with a reference voltage.
The reference voltage is input from the xVREF pins.
The full-scale (100%) chopping current is calculated as follows –
ICHOP = V (xREF) / 5 * R iSENSE
Example:
If a 0.25 ohm sense resistor is used and the VREFx pin is 2.5 V, the full-scale (100%) chopping current will be
2.5 V / (5 x 0.25 ohm) = 2 A.
The reference voltage is scaled by an internal DAC that allows fractional stepping of a bipolar stepper motor.
So as far as our module is concerned, it uses 0.1 ohm resistors as sense resistor so to determine the VREF value we have to use following formula –
VREF = I ( max) * 0.5
One more fact, you have to keep in mind is that if you are using driver in full step mode, the current is limited to 70% of the maximum current limit, so accordingly you have to set the current limit almost 40% higher.
So for example if your stepper motor maximum current is 1A , then
VREF = 1 * 0.5 = 500mV
But if you are using full step mode, then
VREF = 1.4 * 0.5= 0.7 V
So after applying motor power supply, you can set the voltage at the preset at VREF as per your requirement with the help of multimeter and small screwdriver.
Interfacing DRV8825 stepper motor driver module with Arduino
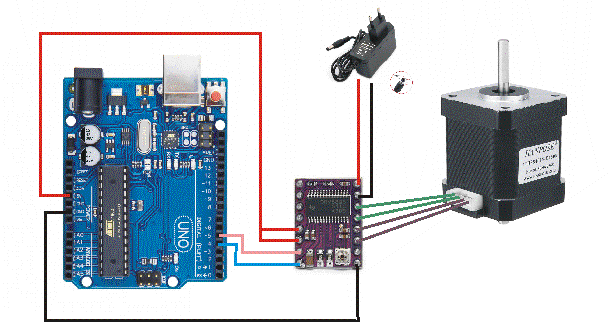
Now that we have understood all the functionality of the module, let us see how we can use this DRV8825 stepper motor driver with Arduino.
Connect Arduino UNO to the driver module as follow –
| Arduino pin | Module pin |
| +5 V | 5 & 6 |
| Gnd | 9 – Gnd |
| 4 | 8 – Direction |
| 5 | 7 – Step |
Now connect the 12 V power supply to module and also connect 4 pin connector to 4 pins of module ( 11,12,13 & 14 ) as shown in above figure.
We keep pins MS1, MS2 & MS3 pins floating so that the module will drive the stepper motor in full step mode. Also we keep Enable pin floating to enable the Driver outputs.
Arduino code for DRV8825 stepper motor driver
Following is the sketch of Arduino. Copy and upload to Arduino to see it functioning.
This sketch will rotate the stepper motor for one revolution clockwise and then one revolution counter clockwise. And this will go on repeating.
// Drive Stepper motor using DRV8825 stepper motor driver
// for more info visit arnin.in
// first define the pins
const int DirPin = 4; // this pin defines direction CW or CCW
const int StepPin = 5; // pulse this pin to move one step
const int SPR = 200; // Steps per revolution
void setup()
{
// Make pins as Outputs
pinMode(StepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DirPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// First let us rotate shaft clockwise
digitalWrite(DirPin, HIGH); // defines the direction to clockwise
// Pulse the step pin
for(int x = 0; x < SPR; x++)
{
digitalWrite(StepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
digitalWrite(StepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
}
delay(1000); // Short delay of one second
// Now rotate shaft counterclockwise
digitalWrite(DirPin, LOW);
// Again pulse the step pin
for(int x = 0; x < SPR; x++)
{
digitalWrite(StepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
digitalWrite(StepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
}
delay(1000); // Short delay of one second
}Code explanation
The above code is self explanatory.
First we define the pins. Make them as Output pins.
Then we decide whether to turn CC or CCW. Accordingly we make the Direction pin High or Low.
Then we pulse the Step pin as per our requirement of revolutions. For example in above example we want one revolution so we multiply that count with 200 ( steps per revolution ) . So we have to provide 1 * 200 = 200 pulses through Step pin to make one revolution.
That is it. It is very easy to drive stepper motors using DRV8825 stepper motor driver module.
Please note that you can also drive stepper motor using A4988 Stepper motor driver module. Interested ? go to A4988 Stepper motor driver with Arduino tutorial .
Try it and if you have any query, do comment below or you can also email to our support team at support@arnin.in to get answers.
Happy Stepping………………..




















+ There are no comments
Add yours