Unveiling the World of Sensors: Exploring Types and Applications
In the ever-evolving realm of technology, sensors stand as indispensable tools, adept at gathering and deciphering data from diverse environments. With a multitude of types and applications, this article delves into the expansive landscape of sensors, shedding light on their diverse roles in various industries.
Exploring the Spectrum: Types of Sensors
Analog vs. Digital: A Fundamental Divide
Sensors find their classification in two primary categories: analog and digital. Analog sensors generate continuous electrical signals, while digital sensors produce discrete electrical signals. Yet, this categorization merely scratches the surface, as the sensor domain boasts myriad types, each distinguished by its unique characteristics and applications.
Unveiling Common Varieties
- Temperature Sensors: Navigating Industries
- Measurement of temperature finds relevance in manufacturing, healthcare, and environmental monitoring.
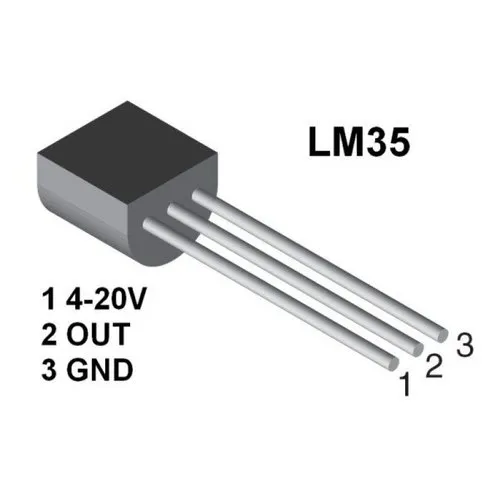
- Pressure Sensors: Powering Precision
- Utilized in pressure measurement, leak detection, and structural monitoring applications.

- Humidity Sensors: Crafting Comfort
- Found in HVAC systems, weather monitoring, and consumer electronics to measure humidity.
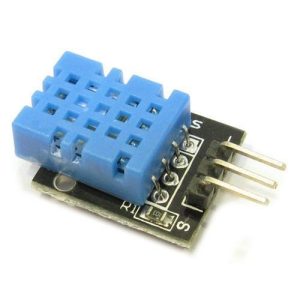
- Proximity Sensors: Pioneering Automation
- Essential in automatic doors, security systems, and industrial automation for detecting object presence.

- Motion Sensors: Driving Innovation
- Crucial in home automation, surveillance systems, and industrial process control for motion detection.

- Gas Sensors: Safeguarding Environments
- Deployed in air quality monitoring, industrial process control, and environmental protection for measuring gas concentrations.

- Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs): Navigating Spatial Realms
- It is applied in navigation, stabilization systems, and virtual reality systems to measure motion in three dimensions.

Navigating the Application Landscape
Healthcare: Pioneering Vitality Monitoring
Sensors find their place in wearable devices, aiding in the monitoring of vital signs, tracking fitness progress, and managing chronic conditions. Additionally, they play a vital role in medical equipment for monitoring and controlling treatments.
Manufacturing: Precision in Production
In the manufacturing sector, sensors drive industrial automation, process control, and quality assurance. They meticulously monitor and control production processes, ensuring optimal performance and product quality.
Environmental Monitoring: Insights into Nature
Sensors contribute to air quality monitoring, water service infrastructure monitoring, and weather monitoring. These applications enable data collection, providing valuable insights for better decision-making and policy development.
Consumer Electronics: Innovating Everyday Devices
Embedded in smartphones, tablets, and other consumer devices, sensors power features like touchscreens, proximity sensing, and motion detection.
Security and Surveillance: Safeguarding Spaces
Sensors play a critical role in security systems, access control systems, and surveillance cameras. They ensure the monitoring and control of access to restricted areas, thereby safeguarding people and property.
Transportation: Navigating the Roads of Safety
Transportation systems, including airplanes, trains, and automobiles, leverage sensors for flight data monitoring, engine diagnostics, and collision avoidance systems.
Agriculture: Cultivating Efficiency
In agriculture, sensors contribute to soil moisture monitoring, crop health monitoring, and irrigation management. Farmers harness these tools to optimize crop production and enhance resource management.
In conclusion, sensors emerge as indispensable components in modern technology, providing invaluable data and insights across diverse applications and industries. Their perpetual evolution and seamless integration into everyday life not only fuel innovation but also deepen our comprehension of the surrounding world.



















+ There are no comments
Add yours